|
David G. Burnet
David Gouverneur Burnet (April 14, 1788 – December 5, 1870) was an early politician within the Republic of Texas, serving as the interim president of Texas in 1836, the second vice president of the Republic of Texas (1839–1841), and the secretary of State (1846) for the new state of Texas after it was annexed to the United States. Burnet was born in Newark, New Jersey, and attended law school in Cincinnati, Ohio. As a young man, he lived with a Comanche tribe for a year before he returned to Ohio. In 1806 Burnet volunteered to serve the unsuccessful filibustering expeditions led by General Francisco de Miranda for the independence of Venezuela from Spain. He fought in Chile in 1807 and in Venezuela in 1808. After Miranda broke with Simon Bolivar, Burnet returned to the United States in 1812. In 1826, he moved to Stephen F. Austin's colony in Mexican Texas. He received a land grant as an empresario but was forced to sell the land after he had failed to attract enough s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of The Republic Of Texas
The president of the Republic of Texas ( es, Presidente de la República de Tejas) was the head of state and head of government while Texas was an independent republic between 1836 and 1845. History and duties The Republic of Texas was formed in 1836. In the midst of the Texas Revolution, Texan settlers elected delegates to the Convention of 1836, which issued the Texas Declaration of Independence and elected David G. Burnet as interim president of the new country. In May 1836 Burnet and Mexican dictator Antonio López de Santa Anna, who was at the time a Texan prisoner-of-war, signed the Treaties of Velasco officially recognizing Texas's break from Mexico. The authority and responsibilities of the president were similar to that of the president of the United States: to serve the people of Texas, and to serve as the head of the military and the state. These were detailed in the Constitution of the Republic of Texas of 1836. The Constitution specified a term of two years for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francisco De Miranda
Sebastián Francisco de Miranda y Rodríguez de Espinoza (28 March 1750 – 14 July 1816), commonly known as Francisco de Miranda (), was a Venezuelan military leader and revolutionary. Although his own plans for the independence of the Spanish American colonies failed, he is regarded as a forerunner of Simón Bolívar, who during the Spanish American wars of independence successfully liberated much of South America. He was known as "The First Universal Venezuelan" and "The Great Universal American". Miranda led a romantic and adventurous life in the general political and intellectual climate that emerged from the Age of Enlightenment that influenced all of the Atlantic Revolutions. He participated in three major historical and political movements of his time: the American Revolutionary War, the French Revolution and the Spanish American wars of independence. He described his experiences over this time in his journal, which reached to 63 bound volumes. An idealist, he develope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harrisburg, Texas
Harrisburg is a community that is now (originally documented as Harrisburgh, then shortened to Harrisburg in 1892) located within the city of Houston, Texas, United States. The community is located east of downtown Houston, south of the Brays Bayou and Buffalo Bayou junction, and west of Brady's Island. It was founded before 1825 on the eastern stretches of the Buffalo Bayou in present-day Harris County, Texas, on land belonging to John Richardson Harris. In 1926, Harrisburg was annexed into the city of Houston. The original name of Harris County was ''Harrisburg (Harrisburgh) County'' until it was shortened after the demise of the ''City of Harrisburg''. Historical markers at the John Richardson Harris site tell of Santa Anna's razing the town on his way through chasing Houston and his retreating army just before they reached Lynch's ferry. History Mexican Texas Harrisburg was surveyed in 1826 and formally named ''Harrisburg'' by its founder, John Richardson Harris. Harris nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convention Of 1836
The Convention of 1836 was the meeting of elected delegates in Washington-on-the-Brazos, Texas in March 1836. The Texas Revolution had begun five months previously, and the interim government, known as the Consultation, had wavered over whether to declare independence from Mexico or pledge to uphold the repudiated Mexican Constitution of 1824. Unlike those of previous Texas councils, delegates to the Convention of 1836 were younger, more recent arrivals to Texas, and more adamant on the question of independence. As delegates prepared to convene, Mexican President Antonio Lopez de Santa Anna led a large army into Texas to quell the revolt; the vanguard of this army arrived at San Antonio de Bexar on February 23. The Convention was called to order on March 1, and the following day adopted the Texas Declaration of Independence, written by George Childress. Delegates elected an interim government, led by President David G. Burnet and developed a Texas Constitution, which they based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington-on-the-Brazos
Washington-on-the-Brazos is an unincorporated community along the Brazos River in Washington County, Texas, United States. The town is best known for being the site of the Convention of 1836 and the signing of the Texas Declaration of Independence. The town is named for Washington, Georgia, itself named for George Washington. It is officially known as just "Washington," but after the Civil War came to be known as "Washington-on-the-Brazos" to distinguish the settlement from "Washington-on-the- Potomac," Washington, DC. History Washington was founded in 1833 by John W. Hall, one of the Old Three Hundred settlers, on land he had been given two years before by his father-in-law Andrew Robinson. It was located at a ferry crossing over the Brazos River on the La Bahia Road that dated from 1821. As the town grew, most settlers were immigrants from the Southern United States, in what was then Mexican Texas. Because of its location on the Brazos River and near major roads, Washington ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
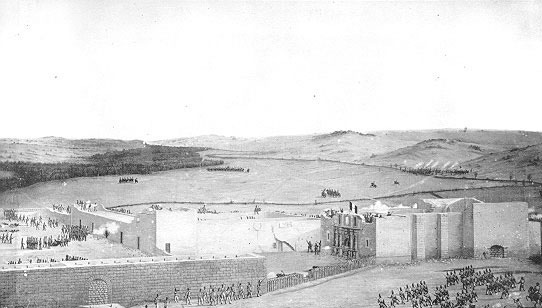
Battle Of The Alamo
The Battle of the Alamo (February 23 – March 6, 1836) was a pivotal event in the Texas Revolution. Following a 13-day siege, Mexican troops under President General Antonio López de Santa Anna reclaimed the Alamo Mission near San Antonio de Béxar (modern-day San Antonio, Texas, United States), killing most of the occupants inside. Santa Anna's refusal to take prisoners during the battle inspired many Texians and Tejanos to join the Texian Army. Motivated by a desire for revenge, as well as their written desire to preserve a border open to immigration and the importation and practice of slavery, the Texians defeated the Mexican Army at the Battle of San Jacinto, on April 21, 1836, ending the rebellion in favor of the newly formed Republic of Texas. Several months previously, Texians, who were primarily recent immigrants from USA, had killed or driven all Mexican troops out of Mexican Texas. About 100 Texians were then garrisoned at the Alamo. The Texian force grew sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
To The People Of Texas & All Americans In The World
To the People of Texas & All Americans in the World is an open letter written on February 24, 1836, by William B. Travis, commander of the Texian forces at the Battle of the Alamo, to settlers in Mexican Texas. The letter is renowned as a "declaration of defiance" and a "masterpiece of American patriotism", and forms part of the history education of Texas schoolchildren. On February 23, the Alamo Mission in San Antonio, Texas had been besieged by Mexican forces led by General Antonio López de Santa Anna. Fearing that his small group of men could not withstand an assault, Travis wrote this letter seeking reinforcements and supplies from supporters. The letter closes with Travis's vow of "Victory or Death!", an emotion which has been both praised and derided by historians. The letter was initially entrusted to courier Albert Martin, who carried it to the town of Gonzales some seventy miles away. Martin added several postscripts to encourage men to reinforce the Alamo, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William B
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the given name ''Wilhelm'' (cf. Proto-Germanic ᚹᛁᛚᛃᚨᚺᛖᛚᛗᚨᛉ, ''*Wiljahelmaz'' > German ''Wilhelm'' and Old Norse ᚢᛁᛚᛋᛅᚼᛅᛚᛘᛅᛋ, ''Vilhjálmr''). By regular sound changes, the native, inherited English form of the name should b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.Gerald O'Collins, O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical rites#Churches, ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and Eparchy, eparchies located List of Catholic dioceses (structured view), around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the Papal supremacy, chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexican Texas
Mexican Texas is the historiographical name used to refer to the era of Texan history between 1821 and 1836, when it was part of Mexico. Mexico gained independence in 1821 after winning its war against Spain, which began in 1810. Initially, Mexican Texas operated similarly to Spanish Texas. Ratification of the 1824 Constitution of Mexico created a federal structure, and the province of Tejas was joined with the province of Coahuila to form the state of Coahuila y Tejas. In 1821, approximately 3,500 settlers lived in the whole of Tejas, concentrated mostly in San Antonio and La Bahia, although authorities had tried to encourage development along the frontier. The settler population was overwhelmingly outnumbered by indigenous people in the province. To increase the number of settlers, Mexico enacted the General Colonization Law in 1824, which enabled all heads of household, regardless of race, religion or immigrant status, to acquire land in Mexico. The first empresaria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen F
Stephen or Steven is a common English given name, first name. It is particularly significant to Christianity, Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( grc-gre, Στέφανος ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is widely regarded as the first martyr (or "protomartyr") of the Christian Church. In English, Stephen is most commonly pronounced as ' (). The name, in both the forms Stephen and Steven, is often shortened to Steve or Stevie (given name), Stevie. The spelling as Stephen can also be pronounced which is from the Greek original version, Stephanos. In English, the female version of the name is Stephanie. Many surnames are derived from the first name, including Template:Stephen-surname, Stephens, Stevens, Stephenson, and Stevenson, all of which mean "Stephen's (son)". In modern times the name has sometimes been given with intentionally non-standard spelling, such as Stevan or Stevon. A common variant of the name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Bolivar
Simon may refer to: People * Simon (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the given name Simon * Simon (surname), including a list of people with the surname Simon * Eugène Simon, French naturalist and the genus authority ''Simon'' * Tribe of Simeon, one of the twelve tribes of Israel Places * Şimon ( hu, links=no, Simon), a village in Bran Commune, Braşov County, Romania * Șimon, a right tributary of the river Turcu in Romania Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Simon'' (1980 film), starring Alan Arkin * ''Simon'' (2004 film), Dutch drama directed by Eddy Terstall Games * ''Simon'' (game), a popular computer game * Simon Says, children's game Literature * ''Simon'' (Sutcliff novel), a children's historical novel written by Rosemary Sutcliff * Simon (Sand novel), an 1835 novel by George Sand * ''Simon Necronomicon'' (1977), a purported grimoire written by an unknown author, with an introduction by a man identified only as "Simon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)